Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
High Pressure Research, 39(3), p.417 - 425, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have developed a technique for neutron diffraction experiments at pressures up to 40 GPa using a Paris-Edinburgh press at the PLANET beamline in J-PARC. To increase the maximum accessible pressure, the diameter of the dimple for sample chamber at the top of the sintered diamond anvils is sequentially reduced from 4.0 mm to 1.0 mm. As a result, the maximum pressure increased and finally reached 40 GPa. By combining this technique with the beam optics which defines the gauge volume, diffraction patterns sufficient for full-structure refinements are obtainable at such pressures.
 H
H - C
- C F
F cocrystal towards graphane structure
cocrystal towards graphane structureWang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; Tang, X.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Lin, X.*; Fang, L.*; Sun, G.*; Chen, X.*; Xie, L.*; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 58(5), p.1468 - 1473, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:80.07(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatics is a novel method to construct sp -carbon frameworks, and nanothreads with diamond-like structures were synthesized by compressing benzene and its derivatives. Here by compressing benzene-hexafluorobenzene cocrystal(CHCF), we identified H-F-substituted graphane with a layered structure in the PIP product. Based on the crystal structure determined from the in situ neutron diffraction and the intermediate products identified by the gas chromatography-mass spectrum, we found that at 20 GPa CHCF forms tilted columns with benzene and hexafluorobenzene stacked alternatively, which leads to a [4+2] polymer, and then transfers to short-range ordered hydrogenated-fluorinated graphane. The reaction process contains [4+2] Diels-Alder, retro-Diels-Alder, and 1-1' coupling, and the former is the key reaction in the PIP. Our studies confirmed the elemental reactions of the CHCF for the first time, which provides a novel insight into the PIP of aromatics.
-carbon frameworks, and nanothreads with diamond-like structures were synthesized by compressing benzene and its derivatives. Here by compressing benzene-hexafluorobenzene cocrystal(CHCF), we identified H-F-substituted graphane with a layered structure in the PIP product. Based on the crystal structure determined from the in situ neutron diffraction and the intermediate products identified by the gas chromatography-mass spectrum, we found that at 20 GPa CHCF forms tilted columns with benzene and hexafluorobenzene stacked alternatively, which leads to a [4+2] polymer, and then transfers to short-range ordered hydrogenated-fluorinated graphane. The reaction process contains [4+2] Diels-Alder, retro-Diels-Alder, and 1-1' coupling, and the former is the key reaction in the PIP. Our studies confirmed the elemental reactions of the CHCF for the first time, which provides a novel insight into the PIP of aromatics.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.301 - 308, 2017/12
PLANET is a neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. Combining the intense neutron source of J-PARC and high-pressure devices designed for time-of-flight powder neutron diffraction enables precise structure analysis of crystal, liquid and amorphous solids over wide pressure and temperature region of 0-20 GPa and 77-2000K. This beamline is effective for various studies in geophysics, planetary science, physics and chemistry. This paper overviews the beamline and introduces recent results obtained at PLANET.
Klotz, S.*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kunc, K.*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 95(17), p.174111_1 - 174111_7, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.61(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The compression behaviour of deuterated ice VII and VIII was investigated by high pressure neutron scattering in the pressure range 2-13.7 GPa between 93 K and 300 K. We establish equations-of-state which contain accurate values for the bulk moduli B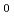 , their pressure derivatives B'
, their pressure derivatives B'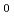 , as well as the ambient pressure volumina V
, as well as the ambient pressure volumina V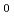 . These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least
. These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least  13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond
13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond 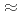 7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this
7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this 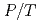 range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*
Hamon, 26(2), p.85 - 90, 2016/05
PLANET is the first neutron powder diffractometer dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature experiments in the World. The six-axis press designed for this beamline enables routine data collection at pressures and temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000K. In this article, we introduce how the PLANET had been constructed.
Hattori, Takanori
Hamon, 25(3), p.231 - 237, 2015/08
PLANET is a time-of-flight (TOF) neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. By using several high-pressure devices, neutron diffraction patterns are obtainable at wide PT condition, ranging from 0-20 GPa and 77 K-2000 K. To obtain clean pattern, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators to eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell. The high performance of the diffractometer with the resolution ( d/d = 0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2-8.4
d/d = 0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2-8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids even under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids even under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
Komatsu, Kazuki*; Shinozaki, Ayako*; Machida, Shinichi*; Matsubayashi, Takuto*; Watanabe, Mao*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 71(1), p.74 - 80, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:79.64(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Magnesium dichloride decahydrate (MgCl 10H
10H O) and its deuterated counterpart (MgCl
O) and its deuterated counterpart (MgCl 10D
10D O) are identified for the first time by in-situ powder synchrotron X-ray and spallation neutron diffraction. These substances are crystallized from a previously unidentified nanocrystalline compound, which originates from an amorphous state at low temperature. A combination of a recently developed autoindexing procedure and the charge-flipping method reveals that the crystal structure of MgCl 10H
O) are identified for the first time by in-situ powder synchrotron X-ray and spallation neutron diffraction. These substances are crystallized from a previously unidentified nanocrystalline compound, which originates from an amorphous state at low temperature. A combination of a recently developed autoindexing procedure and the charge-flipping method reveals that the crystal structure of MgCl 10H O consists of an ABCABC... sequence of Mg(H
O consists of an ABCABC... sequence of Mg(H O)
O) octahedra. The Cl
octahedra. The Cl anions and remaining water molecules unconnected to the Mg
anions and remaining water molecules unconnected to the Mg cations bind the octahedra, similar to other water-rich magnesium dichloride hydrates. The D positions in MgCl
cations bind the octahedra, similar to other water-rich magnesium dichloride hydrates. The D positions in MgCl 10D
10D O, determined by the difference Fourier methods using the neutron powder diffraction patterns at 2.5 GPa, show the features such as bifurcated hydrogen bonds and tetrahedrally coordinated O atoms.
O, determined by the difference Fourier methods using the neutron powder diffraction patterns at 2.5 GPa, show the features such as bifurcated hydrogen bonds and tetrahedrally coordinated O atoms.
Hattori, Takanori; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Junichi*
Bunseki, 2015(2), p.58 - 64, 2015/02
In the J-PARC MLF, 18 beamlines has been constructed and many studies on scientific and industrial use have been performed. This paper introduces the high-pressure science at high-pressure neutron diffractometer "PLANET" and surface/interface structure analysis at vertical sample geometry polarized neutron reflectometer "SHARAKU".
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Tabata, Satoshi*; Kondo, Masahiro*; Nakamura, Akihiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(11), p.113905_1 - 113905_8, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:84.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)We developed a six-axis multi-anvil press, ATSUHIME, for high-pressure and high-temperature in situ time-of-flight neutron powder diffraction experiments. The press has six orthogonally oriented hydraulic rams that operate individually to compress a cubic sample assembly. Experiments indicate that the press can generate pressures up to 9.3 GPa and temperatures up to 2000 K using a 6-6-type cell assembly, with available sample volume of about 50 mm  . Using a 6-8-type cell assembly, the available conditions expand to 16 GPa and 1273 K. Combination of the six-axis press and the collimation devices realized high-quality diffraction pattern with no contamination from the heater or the sample container surrounding the sample. This press constitutes a new tool for using neutron diffraction to study the structures of crystals and liquids under high pressures and temperatures.
. Using a 6-8-type cell assembly, the available conditions expand to 16 GPa and 1273 K. Combination of the six-axis press and the collimation devices realized high-quality diffraction pattern with no contamination from the heater or the sample container surrounding the sample. This press constitutes a new tool for using neutron diffraction to study the structures of crystals and liquids under high pressures and temperatures.
Iizuka, Riko*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Goto, Hirotada*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 218, p.95 - 102, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:33.77(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In situ neutron diffraction measurements combined with the pulsed neutron source at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) were conducted on high-pressure polymorphs of deuterated portlandite (Ca(OD) ) using a Paris-Edinburgh cell and a multi-anvil press. The atomic positions including hydrogen for the unquenchable high-pressure phase at room temperature (phase II') were first clarified. The bent hydrogen bonds under high pressure were consistent with results from Raman spectroscopy. The structure of the high-pressure and high-temperature phase (Phase II) was concordant with that observed previously by another group for a recovered sample. The observations elucidate the phase transition mechanism among the polymorphs, which involves the sliding of CaO polyhedral layers, position modulations of Ca atoms, and recombination of Ca-O bonds accompanied by the reorientation of hydrogen to form more stable hydrogen bonds.
) using a Paris-Edinburgh cell and a multi-anvil press. The atomic positions including hydrogen for the unquenchable high-pressure phase at room temperature (phase II') were first clarified. The bent hydrogen bonds under high pressure were consistent with results from Raman spectroscopy. The structure of the high-pressure and high-temperature phase (Phase II) was concordant with that observed previously by another group for a recovered sample. The observations elucidate the phase transition mechanism among the polymorphs, which involves the sliding of CaO polyhedral layers, position modulations of Ca atoms, and recombination of Ca-O bonds accompanied by the reorientation of hydrogen to form more stable hydrogen bonds.
Proceedings 6th Intern.Symp. on Space Tech. and Sci., p.719 - 728, 1966/00
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Yagafarov, O.*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Chiba, Ayano*; Sano, Asami; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Otomo, Toshiya*; Matsuzaki, Yuki*; Shimojo, Fuyuki*
no journal, ,
PLANET is the beamline dedicated for the high-pressure experiments. The operation has been started at JFY 2013, and now many users are coming to use. In this talk, we introduce the current state of the PLANET and the example of the structure analysis of disordered materials. PLANET adopted the double staged compression system of the multi anvil 6-6, and enables the data collation at 10 GPa and 2000 K. To extend accessible PT range, we newly introduce another compression system of multi-anvil 6-8, and succeeded in generating 16 GPa and 1273 K. In addition, the PLANET is designed so that we can analyze the structure of liquid under pressure. In the analysis, the program for liquid analysis developed at BL21 NOVA is used. Here, we briefly introduce the reliability of the results and the pressure evolution of the silica glass.
 -AlOOH and HD isotope effect
-AlOOH and HD isotope effectSano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
no journal, ,
 -AlOOH is a distorted rutile type hydrous phase. X-ray study have found the change in compressibility at high-pressure, with an isotope effect on the transition pressure. To examine the pressure response of hydrogen bond in
-AlOOH is a distorted rutile type hydrous phase. X-ray study have found the change in compressibility at high-pressure, with an isotope effect on the transition pressure. To examine the pressure response of hydrogen bond in  -AlOOH and its DH isotope difference, we performed neutron diffraction experiments at high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in MLF, J-PARC. The transition from P21nm to Pnnm, which can be attributed to the disorder of hydrogen bond or the symmtrization was found at 12.1 GPa for
-AlOOH and its DH isotope difference, we performed neutron diffraction experiments at high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in MLF, J-PARC. The transition from P21nm to Pnnm, which can be attributed to the disorder of hydrogen bond or the symmtrization was found at 12.1 GPa for  -AlOOD, at the same pressure where the change in compressibility was reported. The significant shortening of O...O distance and hydrogen bond was observed to 12.1 GPa; however, the O...O distance remains almost constant above the transition pressure. This study reveals that slight change of hydrogen position can induce the increase of bulk modulus in
-AlOOD, at the same pressure where the change in compressibility was reported. The significant shortening of O...O distance and hydrogen bond was observed to 12.1 GPa; however, the O...O distance remains almost constant above the transition pressure. This study reveals that slight change of hydrogen position can induce the increase of bulk modulus in  -AlOOH at high pressure.
-AlOOH at high pressure.
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction provides us unique information in the investigation of the structure of materials under high-pressure. However, high-temperature experiments above 10 GPa have not been successful so far because of the conflicting requirements of a sample volume and a sufficient thermal insulation in an internal heater assembly. To overcome this difficulty and extend the accessible PT range, we applied a 6-8 type multi-anvil assembly (MA6-8) to a neutron diffraction experiment. The experiments were conducted using the 6-axis multi-anvil press in the high- pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET. A test with NaCl as an internal pressure standard shows that the pressure reaches to 16 GPa. We also observed the synthesis of CaSiO perovskite from the starting material of wollastonite after the heating at 1100
perovskite from the starting material of wollastonite after the heating at 1100  C at 16 GPa for 3 hours. The results demonstrate the potential utility of the MA6-8 to high temperature experiments.
C at 16 GPa for 3 hours. The results demonstrate the potential utility of the MA6-8 to high temperature experiments.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
High-Pressure Neutron Diffractometer PLANET constructed at BL11 in MLF is the first neutron spectrometer dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature (high-PT) experiments. This aims at revealing the effects of water on the physical properties of the Earth. The beamline is equipped with the multi-anvil press "ATSUHIME" that can generate high-PT condition very stably, and is able to conduct high-PT neutron experiments at 16 GPa and 1000 C. The most characteristic feature of the beamline is, beside the above high-PT generation capability, that we can obtain very clean diffraction patterns with no Bragg peaks from sample surroundings, such as a heater and anvils. These characters enable us to analyze the structure not only of crystals, but also of liquids and amorphous solids. In this talk, I will introduce the performance of the spectrometer, recent results and future plan of the PLANET, together with the history of the construction.
C. The most characteristic feature of the beamline is, beside the above high-PT generation capability, that we can obtain very clean diffraction patterns with no Bragg peaks from sample surroundings, such as a heater and anvils. These characters enable us to analyze the structure not only of crystals, but also of liquids and amorphous solids. In this talk, I will introduce the performance of the spectrometer, recent results and future plan of the PLANET, together with the history of the construction.
Hattori, Takanori
no journal, ,
PLANET is a neutron powder diffraction beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments, which was constructed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility in J-PARC. The most characteristic feature is the capability of structure analysis on crystals, liquids and amorphous solids under high-pressure and high-temperature condition ( 10 GPa, 2000K) using a large multi-anvil press ATSUHIME specially designed for pulsed neutron diffraction experiments. Additionally, the high-pressure experiments can be performed at low temperatures (
10 GPa, 2000K) using a large multi-anvil press ATSUHIME specially designed for pulsed neutron diffraction experiments. Additionally, the high-pressure experiments can be performed at low temperatures ( 77 K) using various types of presses. Because of these unique characters, the PLANET is used in various fields of sciences, such as geophysics and materials science. The details will be introduced in the presentation.
77 K) using various types of presses. Because of these unique characters, the PLANET is used in various fields of sciences, such as geophysics and materials science. The details will be introduced in the presentation.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Kawamura, Seiko
no journal, ,
So far, high-pressure experiments using neutrons were limited due to the incompatible nature of limited neutron flux with tiny high-pressure sample. Intense neutron source of J-PARC is about to change the situation. In this talk, I will introduce the high-pressure diffraction beamline PLANET and recent results. And also, I will show you resent challenges to expand high-pressure activity to other experimental techniques, such as small angles scattering, quasi elastic scattering, and inelastic scattering.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
10 years has passed since the operation of J-PARC, and 5 years has passed since the PLANET started the user program. After the completion of the beamline in 2013, the developments in devices and techniques of the high-pressure neutron experiments have been done. In this talk, the recent developments and current status are introduced.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
The first domestic high-pressure powder neutron diffractometer PLANET celebrated five years since its operation started. Here, we will introduce the current status and subsequent progress. Expansion of measurable PT region: In the experiments using a 6-axis press, in-situ observation at 14 GPa, 1800 K became possible by increasing the anvil strength by shrink fitting and replacing a graphite with a TiC + Al O
O heater. In experiments using the Paris Edinburgh Press (PE press), by reducing the anvil top to 2.5 mm in diameter, experiments at 30 GPa are possible. Improvement of measurement data quality: when using a PE press, samples are normally pressurized together with liquid pressure medium to avoid peak broadening. However, above 10 GPa, the medium solidifies and the peaks are broadened. To fix this problem, a system capable of heating the sample up to 100
heater. In experiments using the Paris Edinburgh Press (PE press), by reducing the anvil top to 2.5 mm in diameter, experiments at 30 GPa are possible. Improvement of measurement data quality: when using a PE press, samples are normally pressurized together with liquid pressure medium to avoid peak broadening. However, above 10 GPa, the medium solidifies and the peaks are broadened. To fix this problem, a system capable of heating the sample up to 100 C was designed and now we can obtain sharp diffraction peaks up to 20 GPa. New measurement method: In order to obtain macroscale information of samples under high PT condition, we attempted neutron radiograph. By using a compact neutron camera, we can place a camera close to the sample and obtain high resolution images.
C was designed and now we can obtain sharp diffraction peaks up to 20 GPa. New measurement method: In order to obtain macroscale information of samples under high PT condition, we attempted neutron radiograph. By using a compact neutron camera, we can place a camera close to the sample and obtain high resolution images.
Hattori, Takanori
no journal, ,
The PLANET is a powder diffraction beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments constructed at MLF in J-PARC. The most important feature is to enable the in-situ observation of the state of matter at high pressure and high temperature (10 GPa, 2000 K) by neutron diffraction and neutron imaging using a 6-axis multi anvil press (max. load is 500 ton per axis). The PLANET is also equipped with a radial collimator with a gauge length of 1.5 mm to 3.0 mm, which make it possible to obtain a clean diffraction pattern without signals from materials around the sample (heater and pressure medium etc.). Thanks to this character, it is possible to analyze the structure of crystals and liquid / amorphous solids very accurately even under high pressure. By exchanging a 6-axis press with a small press, high-pressure experiments are possible over wide temperature range from 77 K to 2000 K. In this lecture, I will introduce recent achievements obtained at the PLANET.